Vetting API
Overview
The E-HAWK Vetting service provides real-time reputation and risk analysis. The Vetting API is used to call the vetting service during sign-up, account updates, logins, or other user interactions. Please follow this guide for implementation instructions.
Endpoint (6.8)
https://api.ehawk.net/
Using HTTPS RESTful calls, your online forms or back-end systems query our service about risks levels associated with the information entered by users.
The API requires HTTPS POST and Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
For all API calls:
- Data is sent with name/value pairs keyword=value
- Properly encode all values within the HTTPS POST
- All values must be in UTF-8 character sets
- x-www-form-urlencoded does not support boolean, so all true/false settings must be strings
curl -X POST -H Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded -d 'apikey=your_apikey&ip=10.1.1.1&email=me@test.com&country=us' https://api.ehawk.net/
Keywords
The Vetting API will analyze the following input values to calculate a Risk Score. Every API call requires the apikey and either an ip, email, domain, or link value. However, the more keyword and value pairs provided, the better and more detailed the analysis. API call Keywords must be lowercase. Please follow value formats listed below.
| Keyword | Value and Format |
|---|---|
| apikey | Your Vetting API KEY (required) |
| ip | IP address of the user connecting browser. IPv6 supported but IPv4 recommended. |
| email address (name@example.com) | |
| talon | See EHawkTalon.js for device fingerprinting implementation |
| phone | US and Canada: 10 digit format XXXXXXXXXX International: "+" AND country code AND number, ex: +33143542331 (France phone) |
| street | Street, PO box, location |
| city | City, town, or village |
| state | State, province, or area. US and Canada must be two-letter lowercase code (example tx=Texas). Other countries just use the actual state if available. |
| postalcode | Postal code or zip code |
| country | Two letter lowercase country code (example us=USA). Be sure to send country value if sending any address data. |
| domain | User’s verified domain. Not necessarily the domain of their email, but the domain they own or will be sending email from. Domain should be linked to their business or “From” address of their emails. Example “ehawk.net”. Do not use URL (no http://, just “domain.com”) If no domain then send the email domain as domain, so jim@aol.com would send domain=aol.com |
| website | URL of the users website (http://www.mysite.com). Send either keyword 'domain' or 'website', but not both. If both sent, we just process domain. |
| link | URI/URL of embedded link to check for possible spam, phishing and other risks. Use fully qualified URLs such as https://www.example.com/webpage.html for links embedded in messages asking users to click. Use the destination URL not a click tracking link created by your system, but the actual URL. |
| firstname | First name (No prefix such as 'Dr.'. No middle initial.) Do not send company names. |
| lastname | Last name (No suffix such as 'Jr.' or 'III') Do not send company names |
| username | The unique username or userID of the account on your systems or platform. Truncated at 50 characters. Do not use email for username. |
| useragent | The User-Agent string provided by the browser |
| lead_id | ID of lead in your lead management system. Max length: 50 characters. |
| lead_source | ID, name, or URL that is providing the leads. Max length: 250 characters. |
| sub_id | Lead Source Sub ID. Max length: 250 characters. |
| campaign_id | Campaign ID or name. Max length: 250 characters. |
| bank_name | Bank name |
| account_number | Bank account number |
| routing_number | Bank routing number. In US this is the ABA. |
| driving_ license_number |
Driver's license number. US only. |
| driving_ license_state |
Two-letter lowercase code for driver's license issue state. US only. |
| birth_date | Birth date in format YYYY-MM-DD. Required for social_ security_number testing. |
| social_ security_number |
Social security number in format 123456789. USA only. |
| revet | true (string not boolean) IMPORTANT! The vetting service by default uses activity testing to tag similar data from multiple sign-ups, bots, etc. If you want to manually vet a user again within a short period of time, you should add revet=true to the API call, so it bypasses the activity tracking engine. Otherwise our system will think the person is trying to sign-up multiple times and start marking that user as high risk. The service will still display any previous activity results but will not increment counters or change activity scoring. Default is false. Must be sent as string, not a boolean. |
| c_Custom_Field_Name | To incorporate other scoring systems or score other non EHAWK data points, you can create Custom Fields with scoring rules in API Key Scoring Profiles. Custom Field names and details are listed in the JSON response and the Portal. Custom Fields are mapped with a prefix c_ |
| backend_max_time | 3000ms (1,000 to 10,000 or API key Setting) The maximum time in milliseconds the API background process (including checking domain content, email deliverability, phone characteristics) will run before timing out. Default is 3000ms. Smaller times might result in missed information and scoring but will speed up the API response. Longer times allow for fewer backend timeouts but can result in slower API calls. This only impacts the time our backend looks for data from external systems. Send with API call will override the API backend_max_time default time in settings. As an example, if the API key default backend_max_time = 3000 and you call the api with backend_max_time=2000, this specific API call will use 2000ms. |
| timeout | false (string not boolean)
This option is replaced with backend_max_time. Use backend_max_time.
If timeout=false then the vetting engine will perform important, additional testing on domain, email, phone and other areas. If you can wait a few seconds
for the API response, then add this to your API calls, as the extra data is valuable. Must be sent as string, not a boolean. Admins can set default as 'false' in the portal so all API calls use 'false'. Default is 'true'.
|
If a keyword is supplied in the API call with no value, or blank, or even a holder value such as “none” or “n/a”, then the Vetting service treats this as suspicious, will score the area negatively, and list the error in the API response. We recommend mandatory fields in forms should be vetted, and optional fields should only be vetted when completed by users. Keywords with no data/empty/placeholders can receive negative scores and impact the Risk Score.
Talon (6.0.8)
The API is supported with a JavaScript device analysis technology. Incorporating this into your forms and sign-up process increases accuracy and provides extra data for E-HAWK to analysis.
When the script runs it will update the value in the hidden field "talon6" in your form. In the form POST you will get a name value pair talon = value. This value (JSON payload) you send to the API together with the other data such as IP, email, etc.
Example implementation where you can see the Talon Generation:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>EHawk Talon</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" name="talon6" id="talon6" value='{"version": 6, "status": -1}'>
<script type="text/javascript">
var eHawkTalonSettings = {
cookie: {
SameSite: 'Lax',
Secure: false,
},
bind: {
OutId: 'talon6',
},
};
</script>
<script src="path_to_your_talon_js_6_file.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
The bind=>OutID value should match the form element id name. When using on your webpages, change the input type to "hidden" and the talon payload will be part of the form POST but not viewable on the form.
Download Talon JS in the portal (Account=>Settings, bottom of page) and add to your JS files or CDN.
Additional Settings
Talon 6.0.8 and higher supports options for autoLoad, cookie key name, and async calls for advanced installations.
- autoLoad: true or false. When set to false, make sure to call Talon.eHawkTalon();
- when wishing to execute code after Talon is completed (previously oncomplete callback in Talon v5), use await when calling Talon.eHawkTalon(), to ensure talon has finished loading
- to customize the name of the cookie key use cookieName
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>EHawk Talon</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" name="talon6" id="talon6" value='{"version": 6, "status": -1}'>
<script type="text/javascript">
var eHawkTalonSettings = {
cookie: {
SameSite: 'Lax',
Secure: false,
},
bind: {
OutId: 'talon6',
},
autoLoad: false,
cookieName: 'talon6',
};
</script>
<script src="path_to_your_talon_js_6_file.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// When autoLoad == false, call Talon manually,
// EITHER by calling it directly:
Talon.eHawkTalon();
// OR by calling it async, but not both:
async function execTalon() {
await Talon.eHawkTalon();
const tal = document.getElementById('talon6');
console.log('talon val', tal.value);
// execute custom code after Talon has finished.
}
execTalon();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Please contact support@ehawk.net for any additional info on the Talon.
Response
The output returned by an API call is in JSON format. There are two response formats that can be selected in the Portal Settings area: Format 2 (new and compact) and Format 1 (original).
{
"version": "6.8",
"transaction_id": "5808be52e52542.29287853",
"status": 0,
"error_message": "",
"score": {
"risk": -100,
"type": "Very High Risk",
"total": -523
},
"area": {
"ip": -80,
"email": -155,
"phone": 5,
"domain": 0,
"geolocation": -24,
"community": -139,
"combo": -25,
"custom": -80,
"fingerprint": -25
},
"fingerprint": {
"id": "15da7f7b71f17e237ff9197e19802399",
"hits": 4
},
"risk_hits": {
"ip": [
"Proxy - Anonymous",
"Spam Blacklist"
],
"email": [
"Disposable",
"Emaildomain Age 1 to 5 Days"
],
"geolocation": [
"IP vs location > 6,000 miles"
],
"activity": [
"4 Repeats"
],
"community": [
"Fraud Email",
"Cyber Crime IP"
],
"combo": [
{
"name": "ip geo EG and free email",
"score": -25,
"details": "filter:Email:Free and value:GeoIPCountry:eg"
}
],
"custom_fields": [
{
"name": "checkCommentForm",
"score": -80,
"details": "contains <a href="
}
]
}
}
A Sample JSON format and areas:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| version | string | API version |
| transaction_id | string | API transaction ID |
| status | number | status code. See codes below |
| error_message | string | blank if no error, or message of error |
| score | array | risk number between -100 and +100 (can change when custom scoring bands used) type string of the Risk Level total number of the total score of all areas |
| area | array | each area tested with the score as a number |
| fingerprint | array | id string value of fingerprint hits number of times seen in API calls |
| risk_hits | array | area arrays with all the hits for each area. Combo and Custom Tests have a special array listing the item names, scoring, and details. |
There can be additional data in the JSON depending on service levels and features. Please make sure to properly parse the JSON response to allow for additional data. The key structure above will not change.
{
"version": "6.8",
"transaction_id": "5808be52e52542.29287853",
"status": 0,
"error_message": "",
"score": [
"Risk Score",
-100,
"Very High Risk"
],
"scores": {
"ip": [
"total",
-250
],
"email": [
"total",
-135
],
"community": [
"total",
-80
],
"combo": [
"total",
-25
],
"custom": [
"total",
-80
],
"geolocation": [
"total",
-65
],
"activity": [
"total",
-65
]
},
"details": {
"score_total": -700,
"fingerprint": "12e30087109e44e4fd4",
"fingerprint_hits": 3,
"ip": {
"score_details": [
"Proxy - Anonymous",
"Bots, Drone, Worm, Proxy, TOR",
"Spam Blacklist"
]
},
"email": {
"score_details": [
"Disposable"
]
},
"geolocation": {
"score_details": [
"IP vs location > 6,000 miles"
]
},
"activity": {
"score_details": [
"4 Repeats"
]
},
"combo": {
"score_details": [
"ip geo = us"
],
"combo_details": [
{
"name": "ip geo EG and free email",
"score": -25,
"details": "filter:Email:Free and value:GeoIPCountry:eg"
}
]
},
"custom_fields": {
"score_details": [
"checkCommentForm"
],
"custom_details": [
{
"name": "checkCommentForm",
"score": -80,
"details": "contains <;a href="
}
]
},
"community": {
"score_details": [
"Fraud Email",
"Cyber Crime IP"
]
}
}
}
The JSON format and areas are:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| version | string | API version - changes with each release |
| transaction_id | string | API transaction ID |
| status | number | status code |
| error_message | string | blank if no error. Message of error. |
| score | array | three elements. Item 1 is a label. Item 2 is the Risk Score (number between -100 and +100 - can change when custom scoring bands used), item 3 is the Risk Type string |
| scores | array | arrays of each scoring area. Array key is area. Item 1 is a label of 'total'. Item 2 is a number value of the area score. |
| details | array | score_total number sum of all scoring fingerprint string value fingerprint_hits number of time fingerprint seen by system area hits if risk hits, then they are listed for each area under score_details array. Combo and Custom Tests have a special array listing the item names, scoring, and details. |
There can be additional data in the JSON depending on service levels and features. Please make sure to properly parse the JSON response to allow for additional data. The key structure above will not change.
Status Codes
The status will be a value (0 = OK) or an error code and a corresponding errors array. Your script should check for status = 0 for a valid API call and response. As an example, an API call with an invalid apikey would return
{
"version":"6.8",
"transaction_id":"123456789",
"status":-3,
"error_message":"Invalid API key"
}
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Success - no errors |
| 5 | API requires either IP, email, or domain inputs
or 'IP input error' (if IP required for API key) |
| -1 | network congestion (reduced fidelity) |
| -3 | Invalid API key |
| -4 | Account Suspended |
| -6 | IP not in ACL |
| -8 | illegal content (data not sent as UTF-8 character sets) |
| -12 | Out of Vetting Credits |
| -13 | Exceeded Max API Call Rate |
| -99 | Database connection error (System issues) |
Sample Code
First, create a web form (form.php) that captures information to send to the API. Here we capture some data such as first and last name and email. We also capture in hidden fields IP, useragent, and talon. Note that the POST values need to match the form name values. When submitted, the form action sends the names and values to 'process.php' that calls the API and processes the scoring and response.
Typically our API responds in about one second. If our services need to contact SMPT or Web servers that are on slow connections, the API can take longer. In the sample code below we set the CURL timeout to 10 seconds. We also recommend adding a queue in your code to call the API with the timeout data again after a few minutes and adding revet=true.
<!-- Sample Form "form.php" - PHP File -->
<form action="process.php" method="POST">
<input type="text" name="firstname">
<input type="text" name="lastname">
<input type="email" name="email">
<input type="hidden" name="talon6" value='{"version": 6, "status": -1}' id="talon6">
<script>
var eHawkTalonSettings = {
cookie: {
SameSite: 'Lax',
Secure: false,
},
bind: {
OutId: 'talon6',
},
};
</script>
<input type="hidden" name="ip" value="<?PHP echo $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'];?>"/>
<input type="hidden" name="useragent" value="<?PHP echo $_SERVER['HTTP_USER_AGENT'];?>" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<form>
<script type="text/javascript" src="path_to_your_talon_js_6_file.js"></script>
<?php
// process.php file
// clear and setup keys and values
unset($post_array);
$post_array = array();
// add a keyword and value for each item to pass in the API call
// the $post_array names should match E-HAWK keywords
// the $_POST values should match the form names exactly
$post_array['apikey'] = 'your_apikey';
$post_array['ip'] = $_POST['ip'];
$post_array['useragent'] = $_POST['useragent'];
$post_array['talon'] = $_POST['talon6'];
$post_array['firstname'] = $_POST['firstname'];
$post_array['lastname'] = $_POST['lastname'];
$post_array['email'] = $_POST['email'];
// if no domain owned by user, then grab from emaildomain:
$post_array['domain'] = substr(strrchr($_POST['email'], "@"), 1);
// Call the API using CURL
$curl = curl_init("https://api.ehawk.net/");
if (!empty($curl)) {
curl_setopt ($curl, CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, true);
curl_setopt ($curl, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt ($curl, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt ($curl, CURLOPT_CONNECTTIMEOUT, 10);
curl_setopt ($curl, CURLOPT_TIMEOUT, 10);
curl_setopt ($curl, CURLOPT_USERAGENT, "E-HAWK API Call");
curl_setopt ($curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $post_array);
$result = curl_exec ($curl);
curl_close ($curl);
}
// print result option - remove after testing
print_r($result);
// process result
$response_array = json_decode($result, true);
// check if API response contains status and responded
if (isset($response_array['status'])) {
// check for status value success or error
if($response_array['status'] == '0' ) {
// check for JSON response format 1 or 2
// JSON Format 1
if(isset($response_array['scores'])) {
echo '<p>Risk Score = '.$response_array['score'][1].'<br>';
echo 'Risk Type = '.$response_array['score'][2].'</p>';
}
// JSON Format 2
if(isset($response_array['area'])) {
echo '<p>Risk Score = '.$response_array['score']['risk'].'<br>';
echo 'Risk Type = '.$response_array['score']['type'].'</p>';
}
} else {
echo '<p>API Status Error: '.$response_array['error_message'].'</p>';
}
} else {
// API did not respond properly. Probably a timeout issue
// Recommend trying to send API call again with revet=true
echo '<p>Did not get a proper response from API</p>';
}
?>
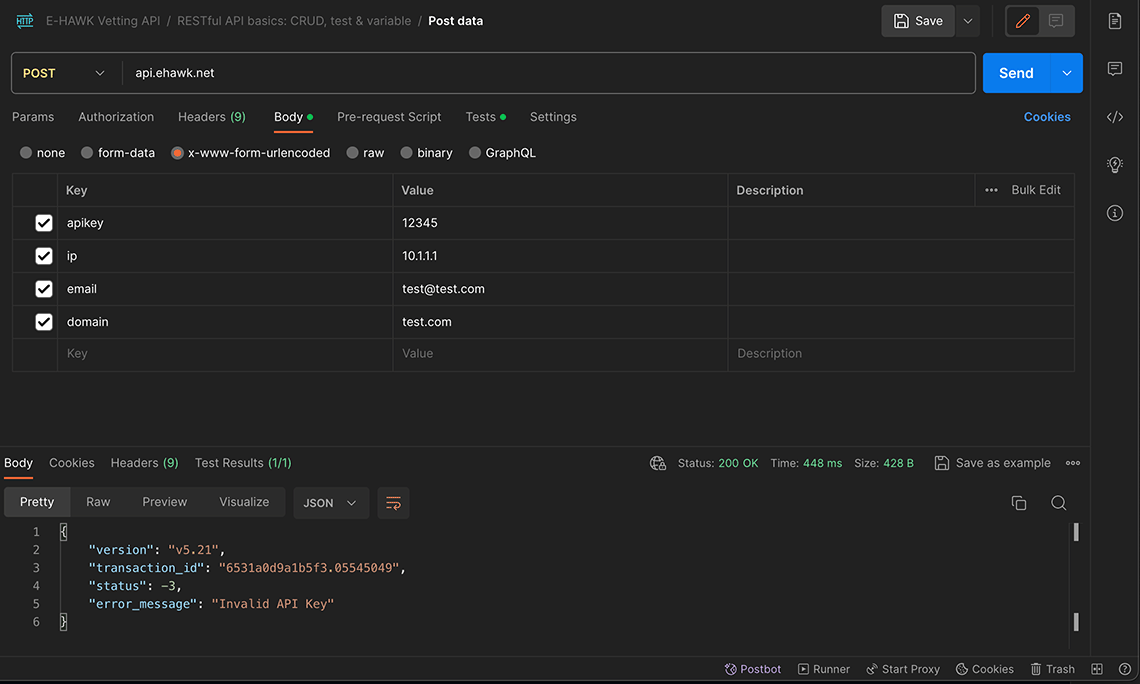
Postman Example
You can test the Vetting API using Postman. Make sure to set post variables as Body and x-www-form-urlencoded.